[September 2025 Web Attack Trend Analysis]
1. Weekly Web Attack Trend Analysis
By analyzing weekly web attack trends, it is possible to identify specific periods when web attacks were concentrated. Based on this, the findings can be used to establish proactive prevention and response strategies to prepare for periods with frequent attacks.
The graph below visualizes the number of web attacks detected by AIWAF on a weekly basis during September 2025.
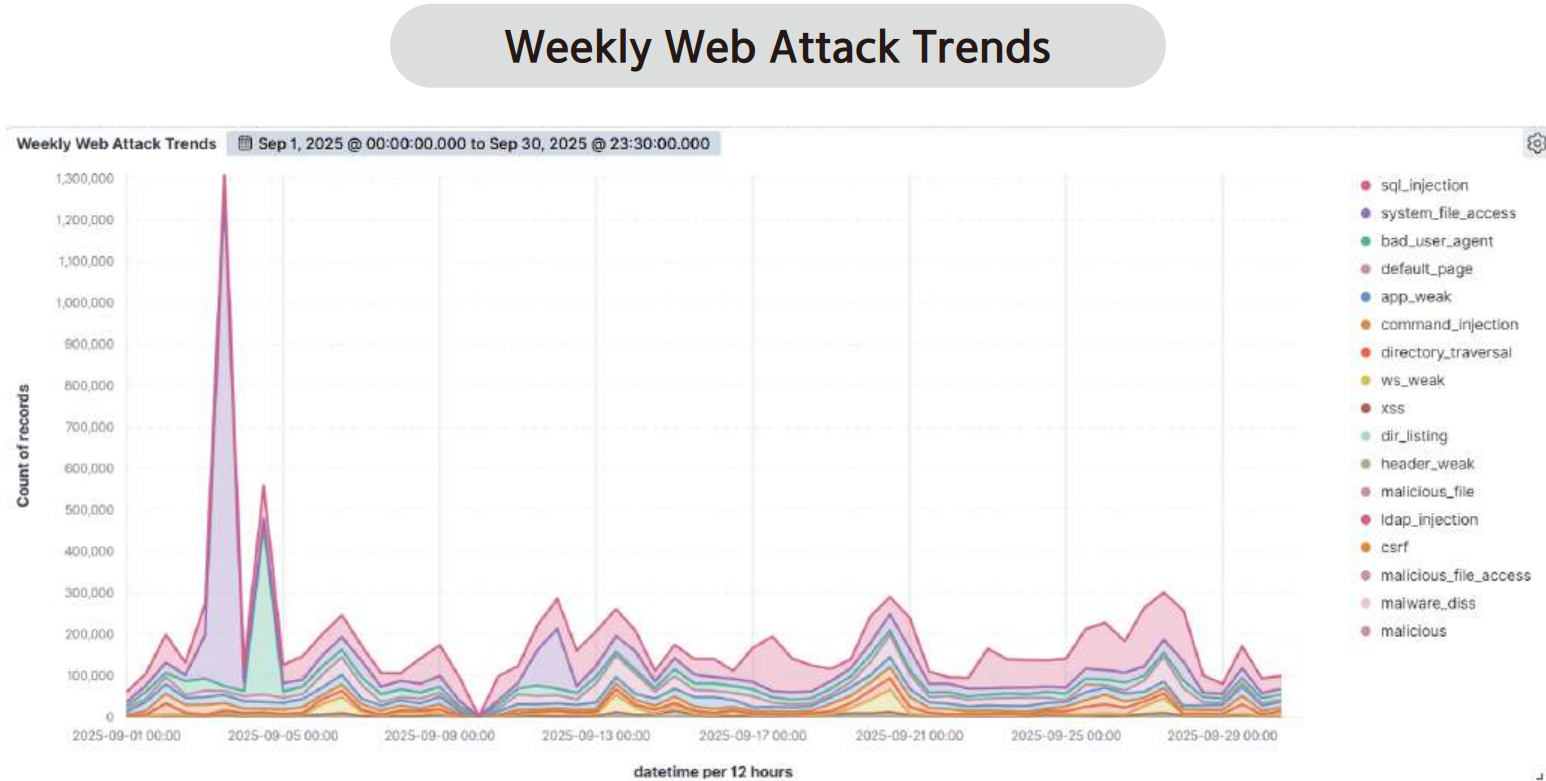
An analysis of the data detected by AIWAF during September 2025 showed that an average of more than 370,000 web attacks were detected per day. This figure reflects a sharp increase compared to the previous month, demonstrating that threats targeting web servers continue to grow in sophistication. In addition, the frequency of attacks was higher on weekends (Saturday and Sunday) than on weekdays, which can be interpreted as a strategic approach that targets periods when web server usage is lower outside of business hours.
In particular, September 3 recorded the highest concentration of web attacks during the entire month, with System File Access attacks accounting for the largest proportion of detections on that day.
Similar to SQL Injection attacks that aim to manipulate databases for privilege escalation or information leakage, System File Access also represents a serious security threat. Through this method, attackers may attempt to read sensitive server configuration files (such as /etc/passwd), application configuration files, log files, or arbitrary files (resulting in information disclosure), and in some cases gain write or execution permissions to escalate privileges within the system. Due to these characteristics, organizations must pay special attention to protecting internal configuration data and user information.
In fact, AIWAF classifies System File Access as a high-risk attack type and includes multiple detection patterns for it. This analysis highlights the need for continuous monitoring and precise response strategies for major web attack types, including system file access vulnerabilities. It will also serve as an important reference for establishing future detection and mitigation policies.
2. Web Attack Trends by Attack Type
By analyzing web attack trends by type based on detection logs, it is possible to systematically identify which types of attacks occurred most frequently during the month. Such analysis goes beyond simple statistics and serves as a key foundation for establishing organizational security policies and formalizing response frameworks.
An analysis of the detection logs collected by AIWAF during September 2025 showed that various types of web attacks were detected, with certain attack categories displaying distinct patterns such as being heavily concentrated during specific periods or accounting for a significant portion of all attacks. Notably, classic yet still highly threatening attack types such as SQL Injection and System File Access ranked among the top. These attacks are typically executed repeatedly, often through automated attack tools or botnets.
The graph below visualizes the distribution of web attack types detected by AIWAF in September 2025.
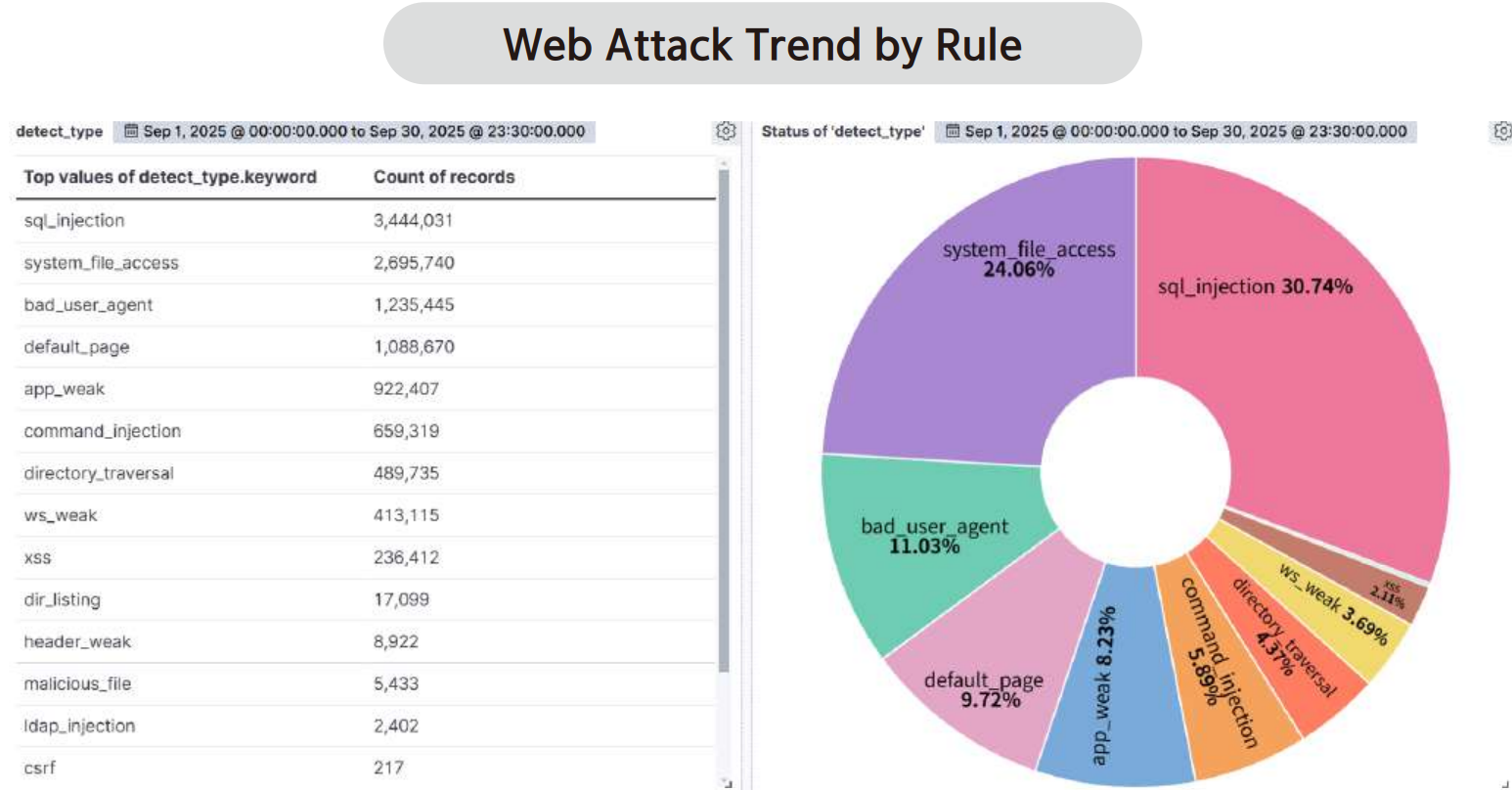
According to the statistics of web attack types detected by AIWAF during September 2025, SQL Injection accounted for 30.74% of total detections, the highest proportion. This was followed by System File Access (24.06%), bad_user_agent (11.03%), Default Page (14.62%), and App Weak (10.06%). These results indicate the need for more precise countermeasures and proactive preventive actions for specific attack types.
First, SQL Injection is a highly critical attack type that consistently ranks near the top of the OWASP Top 10, and its techniques continue to evolve in diverse ways. This attack typically occurs when values supplied via user input are incorporated directly into SQL queries and executed. Attackers exploit this to perform abnormal authentication bypasses, enumerate database structures, and steal sensitive data. Systems that use dynamic queries or lack sufficient input validation are particularly vulnerable to such attacks.
The second most prevalent type, System File Access (24.06%), refers to attempts by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to gain unauthorized access to internal system files and directories or manipulate arbitrary files. These attacks can arise from web server configuration issues, insufficient access controls, or failures in directory path validation. If successful, they can lead to privilege escalation or the installation of backdoors.
The third most prevalent type, Bad User Agent (11.03%), targets requests that use malicious or abnormal User-Agent strings to probe systems or impersonate automated scanners and crawlers. During the reconnaissance phase, an abnormal User-Agent may reveal information about the attacker’s tools or scanning intent (e.g., vulnerability scanning, crawling, scraping), providing clues for subsequent attack activities. This type of traffic often attempts to evade detection by impersonating normal browsers or using known malicious signatures and frequently appears in large-scale automated patterns. Therefore, it cannot be regarded as purely passive. Early detection and blocking are essential since these requests are often generated in high volume by automated scanners.
The fourth most prevalent type, Default Page (9.72%), targets pages that remain in their default state after installation or system message pages. These pages may leak information regarding the type and configuration of system software during the reconnaissance phase, which can be leveraged for further attacks. Although generally passive, this attack type is often executed in bulk using automated scanners, making early detection and response critical.
The fifth most prevalent type, App Weakness (8.23%), exploits inherent security flaws in applications, such as insufficient authentication, session management vulnerabilities, or configuration errors. Notably, there has been an increase in detections involving authentication bypass attempts and API abuse within cloud-based SaaS systems and API-driven services. These trends may have a significant impact on future cloud security policy development.
The Web Attack Trend Report provides the latest web vulnerability analyses, industry-specific attack patterns,
and key CVE-based vulnerability information, all based on processed data from the AI/ML-powered threat intelligence platform AILabs.
Subscribe to receive the full monthly Web Attack Trend Report!
[ Subscribe → ]


