Security tactics for safe online conferences
By Myunghoon Chea
 With the spread of COVID-19, changes have been happening in society, including work, education, and even social life. As the usage of video meeting programs is increasing in companies and schools, the attempts from cyber attackers targeting vulnerabilities of video meeting programs have been increasing rapidly. Thus, we look at the security measures that users can take when using such programs.
With the spread of COVID-19, changes have been happening in society, including work, education, and even social life. As the usage of video meeting programs is increasing in companies and schools, the attempts from cyber attackers targeting vulnerabilities of video meeting programs have been increasing rapidly. Thus, we look at the security measures that users can take when using such programs.
Contents
Zoom Bombing
Video Call Apps
security measure
- Zoom Bombing
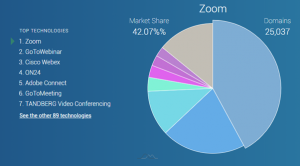 Source: https://www.datanyze.com/market-share/web-conferencing--52
There have been increasing reports on vulnerabilities regarding Zoom, which is the world's largest video conferencing company. Zoom is used in various industries and increasingly so due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
A new term, named “Zoom Bombing,” was named after the software. “Zoom Bombing” refers to any action that interrupts the video call in any way. The attackers can disrupt the meeting by displaying lewd images, shouting profanities, etc. They also yell racial, sexual, or religious slurs along with displaying violent images. Although the term “Zoom Bombing” originated from Zoom software usage, it now refers to any attacks on various video chatting platforms.
The reason that “Zoom Bombing” became a popular term is that the attacks using Zoom's lack of participant authentication became popular worldwide. In general, when an invitation is made to a video participant, an invitation with a link is sent. The invitee can join the meeting by clicking the link. At this time, if the meeting organizer set the conference room without setting a password, joining the room is possible without additional authentication. With the link address, a third party can enter the meeting and intrude. Until recently March, a person could have joined a conference with just an ID and no additional authentication. However, from the 5th of April Zoom made it a default setting to set up a password for a conference ( https://support.zoom.us/hc/en-us/articles/360041408732 ).
As COVID-19 became prevalent around the world, the usage of Zoom software skyrocketed. As a result, the ID addresses (links) were shared on places like social media sites and the attackers were able to acquire them by searching them on search engines or from social media sites or intrude on a conference call using brute force attack.
Also, various security issues are being raised on the Zoom platform, such as the possibility of sensitive information leakage due to end-to-end weak encryption (AES-128), encryption/decryption key via a specific country server, and leakage of personal information of iOS app ( https://www.cnet.com/news/zoom-security-issues-zoom-could-be-vulnerable-to-foreign-surveillance-intel-report-says/ ).
Source: https://www.datanyze.com/market-share/web-conferencing--52
There have been increasing reports on vulnerabilities regarding Zoom, which is the world's largest video conferencing company. Zoom is used in various industries and increasingly so due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
A new term, named “Zoom Bombing,” was named after the software. “Zoom Bombing” refers to any action that interrupts the video call in any way. The attackers can disrupt the meeting by displaying lewd images, shouting profanities, etc. They also yell racial, sexual, or religious slurs along with displaying violent images. Although the term “Zoom Bombing” originated from Zoom software usage, it now refers to any attacks on various video chatting platforms.
The reason that “Zoom Bombing” became a popular term is that the attacks using Zoom's lack of participant authentication became popular worldwide. In general, when an invitation is made to a video participant, an invitation with a link is sent. The invitee can join the meeting by clicking the link. At this time, if the meeting organizer set the conference room without setting a password, joining the room is possible without additional authentication. With the link address, a third party can enter the meeting and intrude. Until recently March, a person could have joined a conference with just an ID and no additional authentication. However, from the 5th of April Zoom made it a default setting to set up a password for a conference ( https://support.zoom.us/hc/en-us/articles/360041408732 ).
As COVID-19 became prevalent around the world, the usage of Zoom software skyrocketed. As a result, the ID addresses (links) were shared on places like social media sites and the attackers were able to acquire them by searching them on search engines or from social media sites or intrude on a conference call using brute force attack.
Also, various security issues are being raised on the Zoom platform, such as the possibility of sensitive information leakage due to end-to-end weak encryption (AES-128), encryption/decryption key via a specific country server, and leakage of personal information of iOS app ( https://www.cnet.com/news/zoom-security-issues-zoom-could-be-vulnerable-to-foreign-surveillance-intel-report-says/ ).
- Video Call Apps
- Zoom ( Zoom)
- Hangout ( Google )
- FaceTime (Apple)
- Skype ( Microsoft )
- Facebook Messenger ( Facebook )
- WhatsApp ( Facebook )
- Houseparty ( Epic Games)
- Discord ( Discord )
- Jitsi Meet ( 8x8 )
- Signal ( Signal Tech )
- Teams ( Microsoft )
- BlueJeans ( Verizon )
- GoToMeeting ( LogMeIn )
- Webex ( Cisco )
- me ( Doxy.me )
- security measures
- Maintaining updated software and OS
- Conference ID protection
- Use the waiting room feature
- Beware of phishing


